HashMap 简介
HashMap 主要用来存放键值对,它基于哈希表的Map接口实现,是常用的Java集合之一。
JDK1.8 之前 HashMap 由 数组+链表 组成的,数组是 HashMap 的主体,链表则是主要为了解决哈希冲突而存在的(“拉链法”解决冲突)。JDK1.8 以后在解决哈希冲突时有了较大的变化,当链表长度大于阈值(默认为 8)时,将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间。
HashMap继承了AbstractMap抽象类,并实现了Map、Cloneable、Serializable接口。
底层数据结构分析
JDK1.8之前
JDK1.8 之前 HashMap 底层是 数组和链表 结合在一起使用也就是 链表散列。HashMap 通过 key 的 hashCode 经过扰动函数处理过后得到 hash 值,然后通过 (n - 1) & hash 判断当前元素存放的位置(这里的 n 指的是数组的长度),如果当前位置存在元素的话,就判断该元素与要存入的元素的 hash 值以及 key 是否相同,如果相同的话,直接覆盖,不相同就通过拉链法解决冲突。
所谓扰动函数指的就是 HashMap 的 hash 方法。使用 hash 方法也就是扰动函数是为了防止一些实现比较差的 hashCode() 方法 换句话说使用扰动函数之后可以减少碰撞。
JDK 1.8 HashMap 的 hash 方法源码:
JDK 1.8 的 hash方法 相比于 JDK 1.7 hash 方法更加简化,但是原理不变。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
|
对比一下 JDK1.7的 HashMap 的 hash 方法源码.
1
2
3
4
| static int hash(int h) {
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
|
相比于 JDK1.8 的 hash 方法 ,JDK 1.7 的 hash 方法的性能会稍差一点点,因为毕竟扰动了 4 次。
所谓 “拉链法” 就是:将链表和数组相结合。也就是说创建一个链表数组,数组中每一格就是一个链表。若遇到哈希冲突,则将冲突的值加到链表中即可。
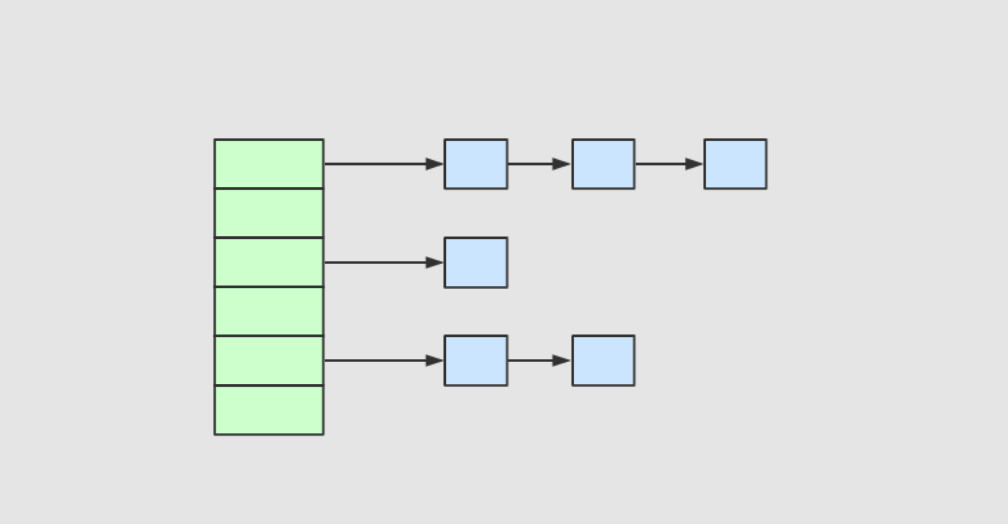
JDK1.8之后
相比于之前的版本,jdk1.8在解决哈希冲突时有了较大的变化,当链表长度大于阈值(默认为8)时,将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间。
HashMap内部属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 362498820763181265L;
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
transient Node<k,v>[] table;
transient Set<map.entry<k,v>> entrySet;
transient int size;
transient int modCount;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
}
|
loadFactor加载因子
loadFactor加载因子是控制数组存放数据的疏密程度,loadFactor越趋近于1,那么 数组中存放的数据(entry)也就越多,也就越密,也就是会让链表的长度增加,loadFactor越小,也就是趋近于0,数组中存放的数据(entry)也就越少,也就越稀疏。
loadFactor太大导致查找元素效率低,太小导致数组的利用率低,存放的数据会很分散。loadFactor的默认值为0.75f是官方给出的一个比较好的临界值。
给定的默认容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75。Map 在使用过程中不断的往里面存放数据,当数量达到了 16 * 0.75 = 12 就需要将当前 16 的容量进行扩容,而扩容这个过程涉及到 rehash、复制数据等操作,所以非常消耗性能。
threshold
threshold = capacity * loadFactor,当Size>=threshold的时候,那么就要考虑对数组的扩增了,也就是说,这个的意思就是 衡量数组是否需要扩增的一个标准。
Node节点类源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
|
树节点类源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent;
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev;
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
|
HashMap源码分析
构造方法
如图,HashMap有以下4个构造方法。
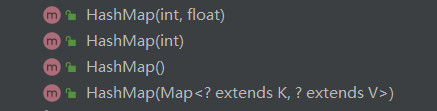
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
}
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
|
putMapEntries方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) {
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
|
put方法
HashMap只提供了put用于添加元素,putVal方法只是给put方法调用的一个方法,并没有提供给用户使用。
对putVal方法添加元素的分析如下:
- 如果定位到的数组位置没有元素,就直接放入。
- 如果定位到的数组位置有元素就和要插入的key比较,如果key相同就直接覆盖,如果key不相同,就判断p是否是一个树节点,如果是,就调用
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value)将元素添加进入。如果不是,就遍历链表插入(即插入的是链表尾部)。在这一过程中如果遇到相同的key,那么就结束遍历过程,覆盖该key对应的value。
putVal方法流程图如下:
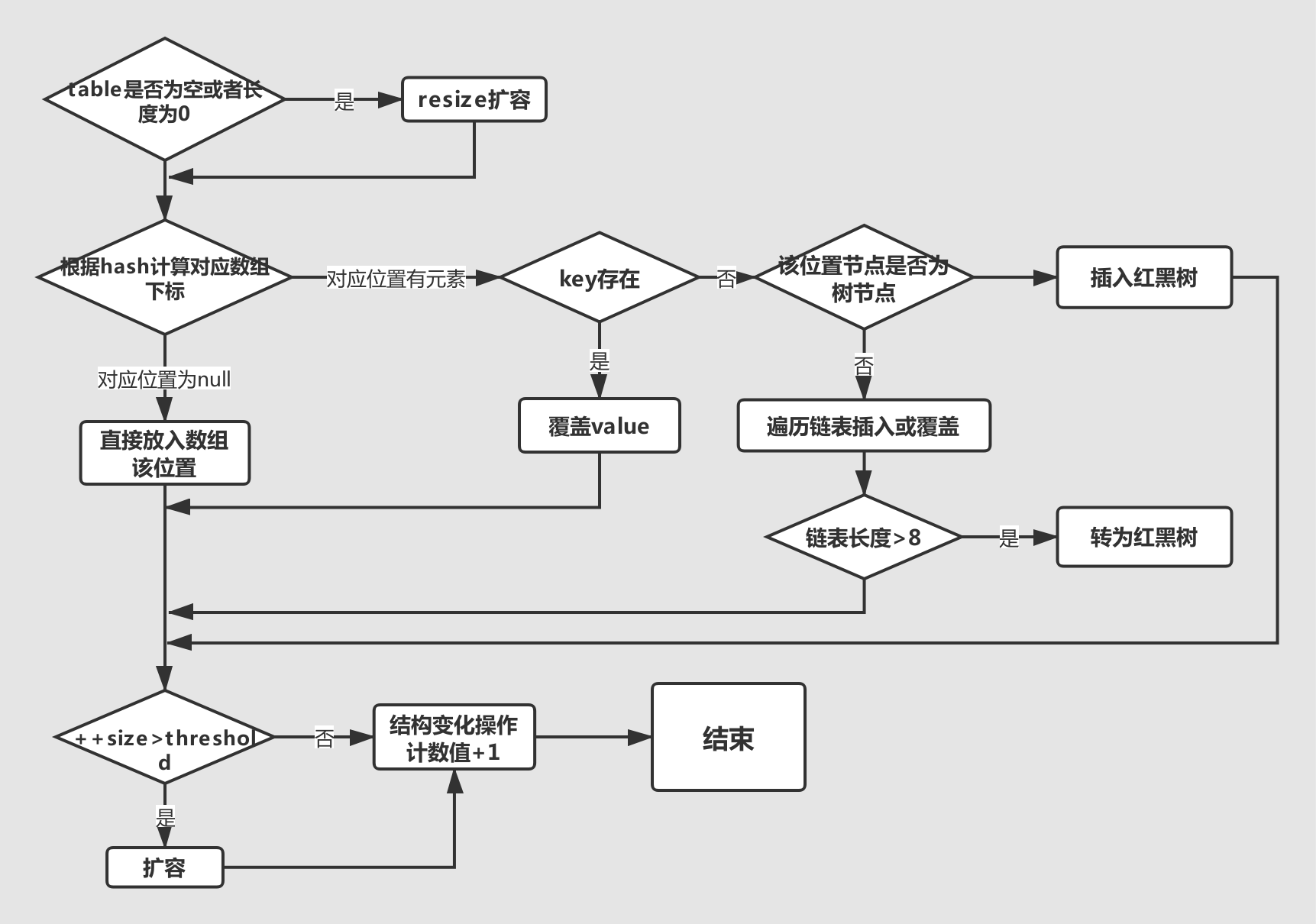
下面分析一下源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
|
我们再来对比一下 JDK1.7 put方法的代码
对于put方法的分析如下:
- 如果定位到的数组位置没有元素,就直接插入。
- 如果定位到的数组位置有元素,遍历以这个元素为头结点的链表,依次和插入的key比较,如果key相同就直接覆盖,不同就采用头插法插入元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public V put(K key, V value)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
|
get方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash &&
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
|
resize方法
进行扩容,会伴随着一次重新hash分配,并且会遍历hash表中所有的元素,是非常耗时的。在编写程序中,要尽量避免resize。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1;
}
else if (oldThr > 0)
newCap = oldThr;
else {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else {
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
|
API
| 返回值类型 |
方法描述 |
void |
clear() 从这张地图中删除所有的映射。 |
Object |
clone() 返回此 HashMap实例的浅拷贝:键和值本身不被克隆。 |
V |
compute(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) 尝试计算用于指定键和其当前映射的值的映射(或 null如果没有当前映射)。 |
V |
computeIfAbsent(K key, Function<? super K,? extends V> mappingFunction) 如果指定的键尚未与值相关联(或映射到 null ),则尝试使用给定的映射函数计算其值,并将其输入到此映射中,除非 null 。 |
V |
computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) 如果指定的密钥的值存在且非空,则尝试计算给定密钥及其当前映射值的新映射。 |
boolean |
containsKey(Object key) 如果此映射包含指定键的映射,则返回 true 。 |
boolean |
containsValue(Object value) 如果此地图将一个或多个键映射到指定值,则返回 true 。 |
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> |
entrySet() 返回此地图中包含的映射的Set视图。 |
void |
forEach(BiConsumer<? super K,? super V> action) 对此映射中的每个条目执行给定的操作,直到所有条目都被处理或操作引发异常。 |
V |
get(Object key) 返回到指定键所映射的值,或 null如果此映射包含该键的映射。 |
V |
getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) 返回到指定键所映射的值,或 defaultValue如果此映射包含该键的映射。 |
boolean |
isEmpty() 如果此地图不包含键值映射,则返回 true 。 |
Set<K> |
keySet() 返回此地图中包含的键的Set视图。 |
V |
merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V,? super V,? extends V> remappingFunction) 如果指定的键尚未与值相关联或与null相关联,则将其与给定的非空值相关联。 |
V |
put(K key, V value) 将指定的值与此映射中的指定键相关联。 |
void |
putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) 将指定地图的所有映射复制到此地图。 |
V |
putIfAbsent(K key, V value) 如果指定的键尚未与某个值相关联(或映射到 null ),则将其与给定值相关联并返回 null ,否则返回当前值。 |
V |
remove(Object key) 从该地图中删除指定键的映射(如果存在)。 |
boolean |
remove(Object key, Object value) 仅当指定的密钥当前映射到指定的值时删除该条目。 |
V |
replace(K key, V value) 只有当目标映射到某个值时,才能替换指定键的条目。 |
boolean |
replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) 仅当当前映射到指定的值时,才能替换指定键的条目。 |
void |
replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K,? super V,? extends V> function) 将每个条目的值替换为对该条目调用给定函数的结果,直到所有条目都被处理或该函数抛出异常。 |
int |
size() 返回此地图中键值映射的数量。 |
Collection<V> |
values() 返回此地图中包含的值的Collection视图。 |